PancakeSwap’s CAKE burn system is designed to help manage the total supply of CAKE by periodically burning (removing) a portion of the minted tokens. The goal is to burn more CAKE than minted, decreasing the token supply. This deflationary approach helps maintain a balanced supply, supporting the token’s long-term health and growth.
We understand that some users have questions about the recent changes to the burn format and how CAKE is managed. Let’s dive into these questions and give you a clearer picture of the key points so you can better understand how the CAKE burn system works and our updates.
1. How Does the New Burn Format (Introduced on March 24th, 2025) Work?
We switched to a simpler format to make it easier to understand the impact of burns on CAKE’s deflationary status. Previously, we reported large amounts of CAKE being burned each week (often over 9M CAKE), but this number only showed the total CAKE burned without factoring in the CAKE that was minted in the same week. As a result, it didn’t fully capture how much CAKE was actually being removed from circulation.
Now, we focus on Net Deflation as the key metric for CAKE’s tokenomics. This method provides a more accurate picture of how much CAKE is actually being reduced from the supply.
Here’s how we calculate it:
Net CAKE Deflation = CAKE Minted (Emitted) to products (like V2 pools, V3 pools, and Lottery) Minus CAKE Burned from products (like V2 pools, V3 pools, Lottery, Prediction, IFOs, and Perpetuals)
For example, our recent burn update reported a net deflation of -339k CAKE, effectively reducing CAKE’s current total supply by 339k, or -0.12%.
Note:
- The Ecosystem Growth Fund is excluded from this calculation until its tokens enter the market. Further details on this can be found in point (3) below.
- Products that generate fees and are processed monthly rather than weekly (e.g., Base pools, Ethereum pools, and IFO-related burns) will cause a sharp increase near the beginning or end of a month as these burns are accounted for
2. Burn Numbers from Week to Week
It’s not uncommon to see some variations between the burn numbers we reported and what is shown on platforms like Dune. This can happen because the amount of CAKE minted each week depends on when the trigger transactions are executed.
For example, CAKE burns take place regularly on Mondays, but since CAKE is minted at a rate of 40 CAKE per block, the amount of CAKE accumulated and sent for minting and burning can vary slightly depending on when the transaction is triggered.
If you look at the Dune Tokenomics chart, you may notice an unusually large net_mint of -3.8M CAKE for the week of March 10th. While this figure is accurate on-chain, about 3M CAKE will be offset when the accumulated CAKE is minted to the Ecosystem Growth Fund during the next burn. As a result, the true net burn for the week of March 10th was around 800K CAKE.
To clarify, when the next burn occurs on Monday, March 31st, the total and circulating supply numbers on Dune will show an increase. However, this doesn’t represent an “additional mint.” The only aspect the team can control is the burn — the minting process is governed by the blockchain and the timing of the transactions.
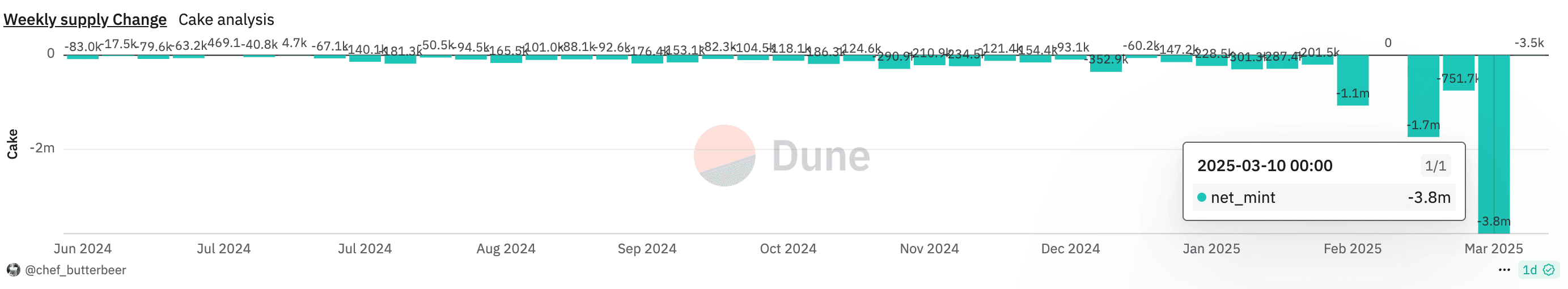
PancakeSwap Tokenomics on Dune
3. Ecosystem Growth Fund
The Ecosystem Growth Fund is not included in the net deflation calculation until its tokens are actually released into the market. This approach helps focus on the tokens that are actively being minted or burned in circulation, giving a clearer picture of CAKE’s real deflationary impact. Including tokens that haven’t entered the market yet could lead to confusion about how much CAKE is actually being reduced from supply.
Currently, the Ecosystem Growth Fund holds 830,625 CAKE, with a total of about 3.8M CAKE accumulated, 3M of which is stored in the MasterChef contract. The primary purpose of this fund is to support farm emissions, but most of this CAKE hasn’t been used yet. Since 2024, less than 1% of the accumulated CAKE has been put to use, while 99% remains idle and hasn’t entered the market. Including the full 3.8M CAKE in the calculation would overstate the amount of CAKE actually circulating.
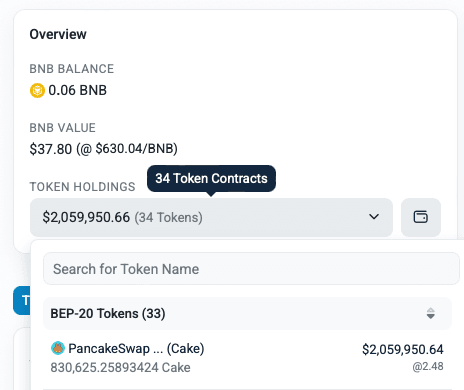
Example of Ecosystem Growth Fund Usage in the past year:
- Base Launch (Sep 2023): Redirected 0.015 CAKE per block from Ecosystem Growth to Base farms.
- CB1 Airdrop: Ongoing at $8,453 every two weeks. Transaction links: BSCScan, Arbiscan, Basescan
- Voting Proposal (Sep 2023): Redirect 0.4 CAKE per block from Ecosystem Growth to Burn, Burn the entire 3M that accumulated until this date. Proposal details
- Locker Protocol Bribes: 500 CAKE per day since April 23, 2024. Proposal link
- PancakeSwap Infinity: Preparation for emissions (~1,200 CAKE per day).
As the fund’s CAKE may be used or burned in the future, excluding it from the current calculation reflects what is actively impacting the circulating supply. When these tokens actually enter the market, they will be considered in the supply, and their use will continue to align with the deflationary goal.
Future Improvements in Burn Reporting and Transparency
To enhance transparency and provide users with a clearer view of the burn process, PancakeSwap will be taking the following steps:
- Open-source Burn Dashboard: We will be developing a dashboard where users can track all emissions and burns, along with their corresponding on-chain transaction hashes. This will allow users to verify the data easily and better understand the changes to CAKE's supply.
- Simplified CAKE Tokenomics Documentation: We will be revising the CAKE tokenomics documentation to provide clearer explanations and make it more user-friendly. The updated documentation will also include a list of all addresses involved in emitting or burning CAKE, offering users a transparent and accessible way to follow the process.
We hope this clarifies the CAKE burn system and answers your questions! As always, PancakeSwap is committed to improving transparency and making the process easier to understand. Stay tuned for more updates, and feel free to share any suggestions or concerns you may have.
The Chef’s
Appendix
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of How CAKE Minting and Burning Works
To give you a clearer understanding of the entire process, here’s a simple breakdown of how CAKE is minted and burned:
Minting:
CAKE tokens are created through the MasterChef contract. Every block on the BNB Chain, 40 CAKE tokens are minted. With 28,800 blocks per day, CAKE is continuously minted throughout the day, but it doesn't happen all at once. Instead, the minted CAKE accumulates and is sent to the burn wallet when triggered.
Burning:
Every Monday, a portion of the minted CAKE is burned (permanently removed from circulation). Most of the tokens are burned directly, but a small portion is allocated toward rewards and ecosystem growth. The CAKE fees generated by PancakeSwap products (like farms, Lottery, etc.) are sent to a multisig wallet, then transferred to a "burn address," which is permanently inaccessible, ensuring that the tokens are gone for good.
Here’s a snapshot of how this works:
Example: Mint and Burn Transactions
Mint Transaction (March 21, 2025) - Automated via Chainlink Job to Fund MCV3:
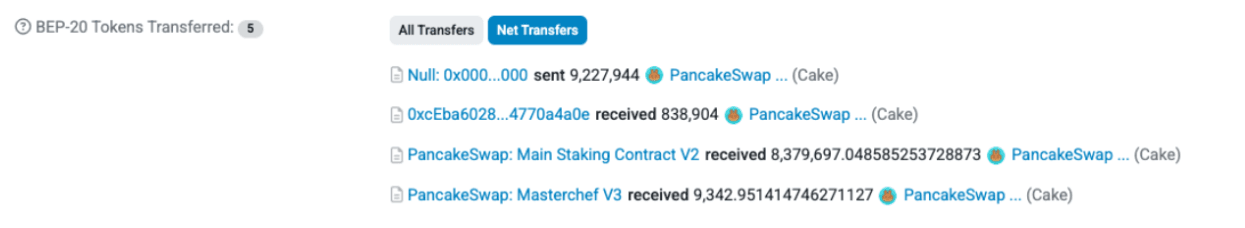
- Burn Address (4a0e): 838,904 CAKE (dev mint, all burned, not transferred anywhere else)
- Main Staking Contract V2: 8,379,697 CAKE (40 CAKE per block, majority burned)
- The gap between the mint (8,379,697 CAKE) and the transfer from the MasterChef v2 contract (7,751,273 CAKE) represents the remaining balance in the MasterChef v2 contract (currently 533,278 CAKE), which is used for emissions (like Farms or Lottery rewards).
Burn Transaction (March 24, 2025):

- Most of the 40 CAKE minted per block (38.637 CAKE) is burned directly.
- 1.363 CAKE is allocated to V2 and V3 farm emissions, Lottery rewards, and the Ecosystem Growth Fund.
- Finally, all the accumulated burn fees are transferred from the burn multisig (4a0e) to the Burn Address, which is permanently inaccessible.
This process helps reduce the total supply of CAKE over time, supporting its deflationary mechanics.